The 2N5457 and PN2222 bipolar serve as voltage isolation devices between the output and the current sensing resistor, R1. The LM101 provides a large amount of loop gain to assure that the circuit acts as a current source. For small values of current (<1 mA), the PN2222 and 10K resistor may be eliminated with the output appearing at the source of the 2N5457.
Precision Current Sink
The 2N5457 JFET and PN2222 bipolar have inherently high output impedance. Using R1 as a current sensing resistor to provide feedback to the LM101 op amp provides a large amount of loop gain for negative feedback to enhance the true current sink nature of this circuit. For small current values, the 10 K resistor and PN2222 may be eliminated if the source of the JFET is connected to R1.
Current Source for Low Resistance Measurements
Current Source
This precision current source has 10 uA to 10 mA ranges with output compliance of 30V to -5V. Output current is fully adjustable on each range with a calibrated, ten-turn potentiometer. Error light indicates saturation.
Introducción
El comportamiento de cualquier circuito eléctrico, del que se conozca su configuración, así como los elementos que lo integran y las condiciones iniciales de funcionamiento, puede determinarse mediante las dos leyes de Kirchhoff y las ecuaciones de tales elementos.
Determinar el comportamiento de un circuito es hallar la expresión de la tensión y de la intensidad correspondiente a cada elemento, conocidas las fuentes de excitación, la carga o la tensión inicial de cada condensador y el flujo o la intensidad de corriente inicial de cada bobina. Para tal fin hemos de plantear y resolver un sistema determinado de ecuaciones.
Determinar el comportamiento de un circuito es hallar la expresión de la tensión y de la intensidad correspondiente a cada elemento, conocidas las fuentes de excitación, la carga o la tensión inicial de cada condensador y el flujo o la intensidad de corriente inicial de cada bobina. Para tal fin hemos de plantear y resolver un sistema determinado de ecuaciones.
Terminología de Redes
Rama: Es un elemento o grupo de elementos que presenta dos terminales. Algunas veces se denomina también lado. Únicamente consideraremos que una agrupación de elementos de dos terminales A y B forma una rama, cuando se conocen los parámetros y la relación que liga la tensión entre A y B con la intensidad que pasa a través de esos terminales. En particular, pueden considerarse constituyendo una rama aquellos elementos que son del mismo tipo, y pueden reducirse a un solo elemento equivalente. La Fig. 1a tiene tres ramas.
Nudo: Es el punto de unión de dos (nudo secundario) o más ramas. A veces se le llama también vértice. En la Fig. 1a, los puntos A y B son nudos, mientras que en la Fig. 1b, los puntos A y B son nudos secundarios.
Lazo: Es un conjunto de ramas que forman una línea cerrada, de tal forma que si se elimina cualquier rama del lazo, el camino queda abierto.
Red plana: Es una red que puede dibujarse sobre una superficie plana sin que se cruce ninguna rama. ¡Ojo!: hay circuitos planos que aparentan no serlo.
Malla: Este concepto se aplica solamente a circuitos planos y es un lazo que no contiene ningún otro en su interior. En un circuito plano existen obviamente tantas mallas como "ventanas" tiene la red. El circuito de la Fig. 2a tiene tres mallas. Compruébese que todas las mallas son lazos, pero no todos los lazos son mallas.
Grafo: Es un dibujo simplificado de un circuito en el que cada rama se representa por un segmento. Si también se indica con una flecha el sentido de la corriente para cada línea del grafo, se dice que se tiene un grafo orientado. La Fig. 2b muestra el grafo de la Fig, 2a.
Circuito conexo: Es aquel circuito en el que se puede pasar de uno de sus nudos a otro cualquiera de ellos, mediante, al menos, una línea continua formada por ramas del propio circuito.
Árbol: Es una parte de un grafo formado por ramas que contengan a todos los nudos, sin que se formen lazos. En la Fig. 2b se han mostrado con líneas continuas un árbol del grafo.
Eslabón: Son las ramas del grafo no incluidas en el árbol. Se conocen también con el nombre de cuerdas o ramas de enlace. Para el grafo de la Fig. 2b, las ramas 1, 5 y 6 son eslabones.
Nudo: Es el punto de unión de dos (nudo secundario) o más ramas. A veces se le llama también vértice. En la Fig. 1a, los puntos A y B son nudos, mientras que en la Fig. 1b, los puntos A y B son nudos secundarios.
Lazo: Es un conjunto de ramas que forman una línea cerrada, de tal forma que si se elimina cualquier rama del lazo, el camino queda abierto.
Red plana: Es una red que puede dibujarse sobre una superficie plana sin que se cruce ninguna rama. ¡Ojo!: hay circuitos planos que aparentan no serlo.
Malla: Este concepto se aplica solamente a circuitos planos y es un lazo que no contiene ningún otro en su interior. En un circuito plano existen obviamente tantas mallas como "ventanas" tiene la red. El circuito de la Fig. 2a tiene tres mallas. Compruébese que todas las mallas son lazos, pero no todos los lazos son mallas.
Grafo: Es un dibujo simplificado de un circuito en el que cada rama se representa por un segmento. Si también se indica con una flecha el sentido de la corriente para cada línea del grafo, se dice que se tiene un grafo orientado. La Fig. 2b muestra el grafo de la Fig, 2a.
Circuito conexo: Es aquel circuito en el que se puede pasar de uno de sus nudos a otro cualquiera de ellos, mediante, al menos, una línea continua formada por ramas del propio circuito.
Árbol: Es una parte de un grafo formado por ramas que contengan a todos los nudos, sin que se formen lazos. En la Fig. 2b se han mostrado con líneas continuas un árbol del grafo.
Eslabón: Son las ramas del grafo no incluidas en el árbol. Se conocen también con el nombre de cuerdas o ramas de enlace. Para el grafo de la Fig. 2b, las ramas 1, 5 y 6 son eslabones.
Análisis de Redes Mediante Ecuaciones de Variables de Rama
El primer paso para el análisis de un circuito está en la determinación de todas las ecuaciones disponibles, de las cuales, posiblemente algunas sean combinaciones lineales del resto, por lo que el paso definitivo será encontrar cuales de entre todas son ecuaciones linealmente independientes.
Número de Ecuaciones Disponibles
Estudiaremos este problema sobre el grafo de un circuito genérico. Admitiremos de momento, que tal circuito es pasivo, y que si hay corrientes circulando por sus ramas, y tensiones entre sus nudos, es debido a la energía inicial almacenada en sus condensadores y en sus bobinas. Posteriormente trataremos el caso general en que existan fuentes de tensión y de intensidad.
Si el circuito tiene r ramas, hay 2r incógnitas, una tensión y una intensidad por cada rama.
Aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff a cada nudo, podemos formular n ecuaciones nodales, y aplicando la segunda ley a cada lazo podemos escribir otras l ecuaciones circulares.
Además, en cada rama, por ejemplo la k-ésima, conocemos la relación uk = uk (ik).
Disponemos, pues, de otras r ecuaciones y, en total, de l+n+r
Ecuaciones Independientes
Para formar un sistema de ecuaciones que sea determinado, necesitamos elegir 2r ecuaciones independientes de entre las (l+n+r).
a)Elección de las ecuaciones nodales:
Existen varios métodos para determinar el número de ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes, pero nosotros usaremos el métodos de los nudos, junto con un teorema que nos dice que "el número máximo de ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes, en un circuito conexo de n nudos, es n-1". Este método consiste en escribir las ecuaciones nodales correspondientes a todos los nudos menos a uno (existe otro teorema que dice que "en un circuito conexo de n nudos, todo conjunto de n-1 ecuaciones, formadas aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff a todos los nudos menos uno, forman un sistema de ecuaciones linealmente independientes").
b)Ecuaciones circulares:
Hemos visto que de las r ecuaciones linealmente independientes, n-1 se obtienen por aplicación de la primera ley de Kirchhoff (ecuaciones nodales). El número máximo de ecuaciones linealmente independientes que podrán obtenerse aplicando la 2ª ley de Kirchhoff (ecuaciones circulares), será, por tanto, r-(n-1). De nuevo, existen dos métodos para esta determinación. Utilizaremos el método de las mallas, el cual se aplica solamente a circuitos planos, y consiste en escribir las ecuaciones correspondientes a todas las mallas. Esto es posible por la existencia de estos dos teoremas:
Teorema: "El número de mallas m de un circuito plano, conexo, de r ramas y n nudos, es igual al de lazos básicos, es decir: m = r - (n - 1)".
Teorema: "Las ecuaciones formadas escribiendo la segunda ley de Kirchhoff para cada malla, son linealmente independientes".
Análisis de Redes. Aplicación
Vamos a ver el procedimiento indicado, para un grafo determinado (el cual no contiene elementos activos). Calcularemos primeramente las ecuaciones nodales y luego las circulares, todo ello para el circuito de la Fig. 3.
a)Las ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes se obtienen aplicando la 1ª ley de Kirchhoff para tres nudos (A, B y C, por ejemplo) de la Fig. 3a:
Nudo A: -i1 + i4 - i5 - i6 = 0
Nudo B: i1 + i2 + i5 = 0
Nudo C: -i2 + i3 + i6 -i7 = 0
(La ecuación, innecesaria, del nudo D sería: -i3 - i4 + i7 = 0)
b)Las ecuaciones circulares linealmente independientes se obtienen aplicando la 2ª ley de Kirchhoff a 4 mallas del circuito de la Fig. 3b (para ello elegimos como intensidades de malla las indicadas a trazos).
Malla 1: u1 - u5 = 0
Malla 2: -u2 + u5 - u6 = 0
Malla 3: u4 + u6 + u7 = 0
Malla 4: - u3 - u7 = 0
Solamente nos faltaría sustituir la ecuación de cada elemento, esto es:
o bien:
(siempre que la flecha de i y de u apunten en el mismo sentido) Con esto, podríamos resolver completamente el circuito, ya que nos queda un sistema de siete ecuaciones con siete incógnitas.
Número de Ecuaciones Disponibles
Estudiaremos este problema sobre el grafo de un circuito genérico. Admitiremos de momento, que tal circuito es pasivo, y que si hay corrientes circulando por sus ramas, y tensiones entre sus nudos, es debido a la energía inicial almacenada en sus condensadores y en sus bobinas. Posteriormente trataremos el caso general en que existan fuentes de tensión y de intensidad.
Si el circuito tiene r ramas, hay 2r incógnitas, una tensión y una intensidad por cada rama.
Aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff a cada nudo, podemos formular n ecuaciones nodales, y aplicando la segunda ley a cada lazo podemos escribir otras l ecuaciones circulares.
Además, en cada rama, por ejemplo la k-ésima, conocemos la relación uk = uk (ik).
Disponemos, pues, de otras r ecuaciones y, en total, de l+n+r
Ecuaciones Independientes
Para formar un sistema de ecuaciones que sea determinado, necesitamos elegir 2r ecuaciones independientes de entre las (l+n+r).
a)Elección de las ecuaciones nodales:
Existen varios métodos para determinar el número de ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes, pero nosotros usaremos el métodos de los nudos, junto con un teorema que nos dice que "el número máximo de ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes, en un circuito conexo de n nudos, es n-1". Este método consiste en escribir las ecuaciones nodales correspondientes a todos los nudos menos a uno (existe otro teorema que dice que "en un circuito conexo de n nudos, todo conjunto de n-1 ecuaciones, formadas aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff a todos los nudos menos uno, forman un sistema de ecuaciones linealmente independientes").
b)Ecuaciones circulares:
Hemos visto que de las r ecuaciones linealmente independientes, n-1 se obtienen por aplicación de la primera ley de Kirchhoff (ecuaciones nodales). El número máximo de ecuaciones linealmente independientes que podrán obtenerse aplicando la 2ª ley de Kirchhoff (ecuaciones circulares), será, por tanto, r-(n-1). De nuevo, existen dos métodos para esta determinación. Utilizaremos el método de las mallas, el cual se aplica solamente a circuitos planos, y consiste en escribir las ecuaciones correspondientes a todas las mallas. Esto es posible por la existencia de estos dos teoremas:
Teorema: "El número de mallas m de un circuito plano, conexo, de r ramas y n nudos, es igual al de lazos básicos, es decir: m = r - (n - 1)".
Teorema: "Las ecuaciones formadas escribiendo la segunda ley de Kirchhoff para cada malla, son linealmente independientes".
Análisis de Redes. Aplicación
Vamos a ver el procedimiento indicado, para un grafo determinado (el cual no contiene elementos activos). Calcularemos primeramente las ecuaciones nodales y luego las circulares, todo ello para el circuito de la Fig. 3.
a)Las ecuaciones nodales linealmente independientes se obtienen aplicando la 1ª ley de Kirchhoff para tres nudos (A, B y C, por ejemplo) de la Fig. 3a:
Nudo A: -i1 + i4 - i5 - i6 = 0
Nudo B: i1 + i2 + i5 = 0
Nudo C: -i2 + i3 + i6 -i7 = 0
(La ecuación, innecesaria, del nudo D sería: -i3 - i4 + i7 = 0)
b)Las ecuaciones circulares linealmente independientes se obtienen aplicando la 2ª ley de Kirchhoff a 4 mallas del circuito de la Fig. 3b (para ello elegimos como intensidades de malla las indicadas a trazos).
Malla 1: u1 - u5 = 0
Malla 2: -u2 + u5 - u6 = 0
Malla 3: u4 + u6 + u7 = 0
Malla 4: - u3 - u7 = 0
Solamente nos faltaría sustituir la ecuación de cada elemento, esto es:
o bien:
(siempre que la flecha de i y de u apunten en el mismo sentido) Con esto, podríamos resolver completamente el circuito, ya que nos queda un sistema de siete ecuaciones con siete incógnitas.
Ramas con Fuentes. Ecuaciones de Definición
En todo circuito con elementos disipativos, es decir, con resistencias, la corriente se mantiene a expensas de fuentes que van proporcionando la energía que se disipa.
Puede darse el caso, como hemos indicado antes, de corriente producida a costa de la energía almacenada inicialmente en algún elemento no disipativo del circuito, pero esta energía ha de estar necesariamente acotada, por lo que la corriente debida a esta causa se ha de extinguir pasado un tiempo más o menos largo. Vamos a estudiar aquí el planteamiento de las ecuaciones correspondientes a circuitos con ramas activas, esto es, ramas con fuentes energéticas, ya sean de tensión o de intensidad.
Si consideramos la existencia de ramas activas, es decir, que contengan fuentes de tensión, de intensidad, o de ambos tipos, lo dicho hasta aquí referente a la selección de ecuaciones nodales y circulares permanece totalmente válido.
En lo que respecta a las r ecuaciones de rama, si éstas eran pasivas, adoptaban la forma u = Z(D)·i, o bien i = Y(D)·u, respectivamente. Si las ramas son activas, seguirá existiendo, en general, una relación entre la tensión e intensidad de cada rama, aunque dicha relación adopte una forma diferente. Estudiaremos los diversos tipos de ramas activas que pueden darse en un circuito, viendo la influencia de los mismos sobre el número de ecuaciones y de incógnitas.
En la Fig. 4 se ha representado un tipo general de rama activa, formada por una fuente de intensidad, conectada en paralelo con un conjunto constituido por la conexión serie de una fuente ideal de tensión y un elemento pasivo, que vendrá definido por su impedancia o admitancia operacional. Calculemos las relaciones entre la tensión de rama, u y la intensidad de rama i, tomando una u otra como variable independiente y admitiendo que el elemento pasivo no está acoplado magnéticamente con otros elementos del circuito que se considere.
Para la asociación serie de la fuente de tensión y el elemento pasivo, podemos escribir, teniendo en cuenta la segunda ley de Kirchhoff:
y aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff al nudo A
Operando ambas ecuaciones obtenemos:
que da la tensión de rama, en función de la intensidad de rama, o bien
que da la intensidad de rama en función de la tensión de rama.
Las ecuaciones 5 y 6 son más generales que las 1 y 2, convirtiéndose en estas en el caso de que ig = 0 y eg = 0, ya que entonces la rama sería pasiva. Este tipo de rama no introduciría ninguna variación en el número de incógnitas (dos por rama), ni en el número de ecuaciones disponibles, pero ahora, la existencia de ig y eg se traduce en existencia de términos independientes, distintos de cero, en las ecuaciones de rama.
En la Fig. 5 se han representado dos tipos de ramas activas, que se obtienen del general, haciendo eg = 0 (cortocircuito) en (a), o ig = 0 (circuito abierto) en (b). Las relaciones que se tendrían ahora para cada rama serían:
Las relaciones tensión intensidad serían, para la rama da la Fig. 5a:
y para la de la Fig. 5b
Como veremos más adelante, en ocasiones convendrá, por simplificación, reducir cualquier tipo de ramas activas a uno de estos dos. Se aconseja acostumbrarse a escribir directamente las expresiones 7 y 8, por aplicación de las leyes de Kirchhoff.
Nótese la analogía entre ambas expresiones si se intercambia tensión por intensidad e impedancia por admitancia. Obsérvese también que las fuentes reales de intensidad (fuente ideal con elemento en paralelo), y las fuentes reales de tensión (fuente ideal con elemento en serie), responden a los tipos de rama de la Fig. 5a y 5b, respectivamente.
Si no existiese el elemento pasivo, es decir, si Y = 0 (circuito abierto), en la Fig. 5a, o Z = 0 (cortocircuito) en la Fig. 5b, tendríamos los tipos de rama de la Fig. 6a y 6b, respectivamente.
Para la primera de ellas la intensidad de rama es conocida: i = ig , existiendo, por tanto, una incógnita menos. La tensión u, sin embargo, sigue siendo incógnita, y su valor dependerá del resto del circuito. Para la segunda (Fig. 6b) la tensión de rama es conocida: u = -eg , existiendo también una incógnita menos. La intensidad i sigue siendo una incógnita, y su valor dependerá del resto del circuito. En ambos casos se tiene una incógnita menos, pero también se dispone de una ecuación menos, ya que no existe relación entre la tensión e intensidad de rama.
Puede darse el caso, como hemos indicado antes, de corriente producida a costa de la energía almacenada inicialmente en algún elemento no disipativo del circuito, pero esta energía ha de estar necesariamente acotada, por lo que la corriente debida a esta causa se ha de extinguir pasado un tiempo más o menos largo. Vamos a estudiar aquí el planteamiento de las ecuaciones correspondientes a circuitos con ramas activas, esto es, ramas con fuentes energéticas, ya sean de tensión o de intensidad.
Si consideramos la existencia de ramas activas, es decir, que contengan fuentes de tensión, de intensidad, o de ambos tipos, lo dicho hasta aquí referente a la selección de ecuaciones nodales y circulares permanece totalmente válido.
En lo que respecta a las r ecuaciones de rama, si éstas eran pasivas, adoptaban la forma u = Z(D)·i, o bien i = Y(D)·u, respectivamente. Si las ramas son activas, seguirá existiendo, en general, una relación entre la tensión e intensidad de cada rama, aunque dicha relación adopte una forma diferente. Estudiaremos los diversos tipos de ramas activas que pueden darse en un circuito, viendo la influencia de los mismos sobre el número de ecuaciones y de incógnitas.
En la Fig. 4 se ha representado un tipo general de rama activa, formada por una fuente de intensidad, conectada en paralelo con un conjunto constituido por la conexión serie de una fuente ideal de tensión y un elemento pasivo, que vendrá definido por su impedancia o admitancia operacional. Calculemos las relaciones entre la tensión de rama, u y la intensidad de rama i, tomando una u otra como variable independiente y admitiendo que el elemento pasivo no está acoplado magnéticamente con otros elementos del circuito que se considere.
Para la asociación serie de la fuente de tensión y el elemento pasivo, podemos escribir, teniendo en cuenta la segunda ley de Kirchhoff:
y aplicando la primera ley de Kirchhoff al nudo A
Operando ambas ecuaciones obtenemos:
que da la tensión de rama, en función de la intensidad de rama, o bien
que da la intensidad de rama en función de la tensión de rama.
Las ecuaciones 5 y 6 son más generales que las 1 y 2, convirtiéndose en estas en el caso de que ig = 0 y eg = 0, ya que entonces la rama sería pasiva. Este tipo de rama no introduciría ninguna variación en el número de incógnitas (dos por rama), ni en el número de ecuaciones disponibles, pero ahora, la existencia de ig y eg se traduce en existencia de términos independientes, distintos de cero, en las ecuaciones de rama.
En la Fig. 5 se han representado dos tipos de ramas activas, que se obtienen del general, haciendo eg = 0 (cortocircuito) en (a), o ig = 0 (circuito abierto) en (b). Las relaciones que se tendrían ahora para cada rama serían:
Las relaciones tensión intensidad serían, para la rama da la Fig. 5a:
y para la de la Fig. 5b
Como veremos más adelante, en ocasiones convendrá, por simplificación, reducir cualquier tipo de ramas activas a uno de estos dos. Se aconseja acostumbrarse a escribir directamente las expresiones 7 y 8, por aplicación de las leyes de Kirchhoff.
Nótese la analogía entre ambas expresiones si se intercambia tensión por intensidad e impedancia por admitancia. Obsérvese también que las fuentes reales de intensidad (fuente ideal con elemento en paralelo), y las fuentes reales de tensión (fuente ideal con elemento en serie), responden a los tipos de rama de la Fig. 5a y 5b, respectivamente.
Si no existiese el elemento pasivo, es decir, si Y = 0 (circuito abierto), en la Fig. 5a, o Z = 0 (cortocircuito) en la Fig. 5b, tendríamos los tipos de rama de la Fig. 6a y 6b, respectivamente.
Para la primera de ellas la intensidad de rama es conocida: i = ig , existiendo, por tanto, una incógnita menos. La tensión u, sin embargo, sigue siendo incógnita, y su valor dependerá del resto del circuito. Para la segunda (Fig. 6b) la tensión de rama es conocida: u = -eg , existiendo también una incógnita menos. La intensidad i sigue siendo una incógnita, y su valor dependerá del resto del circuito. En ambos casos se tiene una incógnita menos, pero también se dispone de una ecuación menos, ya que no existe relación entre la tensión e intensidad de rama.
Modificaciones de la Geometría de un Circuito
En ocasiones, debido en general a hipótesis simplificadoras, podrán aparecer en un circuito ramas activas en que se tiene un elemento en serie con un generador de intensidad ideal, o bien un generador de tensión ideal en paralelo con otro elemento. En ambos casos, ya vimos que, a efectos del resto de circuito, esos elementos pueden quitarse en el análisis, por lo que volveríamos a tener la Fig. 6. (Esto es válido siempre que el elemento no presente acoplamiento magnético con el resto del circuito).
En cuanto a asociaciones de generadores de tensión entre sí o de intensidad, ya vimos las situaciones posibles y las que no lo son. Para poder efectuar la transformación de fuentes es necesario la existencia de un elemento pasivo en serie con la fuente de tensión o en paralelo con la de intensidad.
En el caso de que una rama de un circuito esté formada por una fuente ideal de tensión, dependiente o independiente, sin ningún elemento en serie, estudiaremos la forma de eliminar dicha rama sin que varíe la tensión e intensidad en el resto de los elementos del circuito. Igualmente, caso de que una rama de un circuito esté formada por una fuente ideal de intensidad, dependiente o independiente, sin ningún elemento en paralelo, estudiaremos la forma de eliminar dicha rama sin que varíe la tensión e intensidad en el resto de los elementos del circuito.
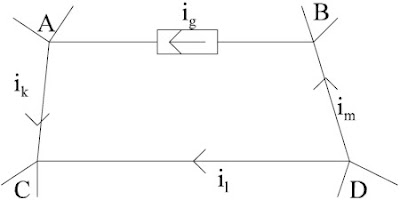
Consideremos primero este segundo caso, representado en la Fig. 7,donde la rama A-B está formada por una fuente de intensidad, ig. Las ramas k, l y m de la citada figura son un conjunto de ramas que forman un lazo con dicha rama A-B. La fuente de intensidad excita el resto del circuito introduciendo por A una intensidad ig que extrae de B.
Esto mismo se consigue en el circuito transformado de la Fig. 8, ya que ig entra y sale de C y D y las fuentes no aportan nada a estos nudos. En consecuencia, a excepción de la fuente de intensidad, todos los restantes elementos del circuito se comportarán igualmente y, por tanto, la tensión uAB será la misma en ambos. Una vez resuelto el circuito de la Fig. 8, la tensión de la fuente del circuito original (Fig. 7) se puede obtener teniendo en cuenta que

que multiplicando ambos miembros por ig nos indica que la potencia suministrada coincide con la suma de las potencias entregadas a cada rama.
El lazo elegido en la Fig. 8 para transportar la intensidad ig desde el nudo B al A, mediante fuentes de intensidad en paralelo con ramas del mismo, puede ser cualquiera que se cierre sobre la rama A-B.
Consideremos ahora el caso representado en la Fig. 9, donde la rama A-B está formada por una fuente ideal de tensión eg. Las ramas k, l y m de la citada figura son el conjunto de todas las ramas que, junto con la A-B, concurren en uno de los extremos de ésta. La fuente de tensión excita el resto del circuito haciendo que el potencial de B exceda al de A en uBA = eg.
En el circuito transformado de la Fig. 10, los nudos Bk, Bl y Bm están todos al mismo potencial uBA = eg respecto de A, por lo que da igual considerarlos unidos o separados. Esto es, el sistema de tres fuentes iguales de la Fig. 10 excita al resto del circuito de igual forma que una sola fuente de la Fig. 9. En consecuencia, los elementos externos a la fuente se comportan igualmente en una y otra configuración. Se observa que iAB = ik -il + im con lo que, multiplicando ambos miembros por eg, llegamos a que la potencia suministrada por la fuente del circuito de la Fig. 9 es igual a la suministrada por las fuentes del circuito de la Fig. 10, con lo que se comprueba que el circuito conectado a las fuentes recibe la misma aportación energética en uno y otro caso.
En cuanto a asociaciones de generadores de tensión entre sí o de intensidad, ya vimos las situaciones posibles y las que no lo son. Para poder efectuar la transformación de fuentes es necesario la existencia de un elemento pasivo en serie con la fuente de tensión o en paralelo con la de intensidad.
En el caso de que una rama de un circuito esté formada por una fuente ideal de tensión, dependiente o independiente, sin ningún elemento en serie, estudiaremos la forma de eliminar dicha rama sin que varíe la tensión e intensidad en el resto de los elementos del circuito. Igualmente, caso de que una rama de un circuito esté formada por una fuente ideal de intensidad, dependiente o independiente, sin ningún elemento en paralelo, estudiaremos la forma de eliminar dicha rama sin que varíe la tensión e intensidad en el resto de los elementos del circuito.
Consideremos primero este segundo caso, representado en la Fig. 7,donde la rama A-B está formada por una fuente de intensidad, ig. Las ramas k, l y m de la citada figura son un conjunto de ramas que forman un lazo con dicha rama A-B. La fuente de intensidad excita el resto del circuito introduciendo por A una intensidad ig que extrae de B.
Esto mismo se consigue en el circuito transformado de la Fig. 8, ya que ig entra y sale de C y D y las fuentes no aportan nada a estos nudos. En consecuencia, a excepción de la fuente de intensidad, todos los restantes elementos del circuito se comportarán igualmente y, por tanto, la tensión uAB será la misma en ambos. Una vez resuelto el circuito de la Fig. 8, la tensión de la fuente del circuito original (Fig. 7) se puede obtener teniendo en cuenta que

que multiplicando ambos miembros por ig nos indica que la potencia suministrada coincide con la suma de las potencias entregadas a cada rama.
El lazo elegido en la Fig. 8 para transportar la intensidad ig desde el nudo B al A, mediante fuentes de intensidad en paralelo con ramas del mismo, puede ser cualquiera que se cierre sobre la rama A-B.
Consideremos ahora el caso representado en la Fig. 9, donde la rama A-B está formada por una fuente ideal de tensión eg. Las ramas k, l y m de la citada figura son el conjunto de todas las ramas que, junto con la A-B, concurren en uno de los extremos de ésta. La fuente de tensión excita el resto del circuito haciendo que el potencial de B exceda al de A en uBA = eg.
En el circuito transformado de la Fig. 10, los nudos Bk, Bl y Bm están todos al mismo potencial uBA = eg respecto de A, por lo que da igual considerarlos unidos o separados. Esto es, el sistema de tres fuentes iguales de la Fig. 10 excita al resto del circuito de igual forma que una sola fuente de la Fig. 9. En consecuencia, los elementos externos a la fuente se comportan igualmente en una y otra configuración. Se observa que iAB = ik -il + im con lo que, multiplicando ambos miembros por eg, llegamos a que la potencia suministrada por la fuente del circuito de la Fig. 9 es igual a la suministrada por las fuentes del circuito de la Fig. 10, con lo que se comprueba que el circuito conectado a las fuentes recibe la misma aportación energética en uno y otro caso.
Circuitos Duales
La Teoría de Circuitos tiene como fundamentales las Leyes de Kirchhoff:
1ª Ley: La suma algebraica de las intensidades que circulan por todas las ramas que cortan un recinto cerrado es igual a cero: Σi = 0.
2ª Ley: La suma algebraica de las tensiones de las ramas que forman un circuito cerrado es igual a cero: Σu = 0.
Se observa la dualidad entre estas leyes básicas con las palabras tensiónintensidad y recinto cerrado-circuito cerrado que pueden considerarse como conceptos duales básicos.
Como se ve, la dualidad queda reflejada en las ecuaciones matemáticas, por simple intercambio de las variables duales.
Configuraciones duales:
Considerando el espacio exterior de todo circuito plano como una malla adicional (supóngase que el circuito reposa sobre una esfera)limitada por las ramas externas, se dice que dos circuitos tienen configuraciones duales cuando las ecuaciones que resultan de aplicar la 1ª/2ª ley de Kirchhoff a todos los nudos/mallas (incluida la exterior), de uno de ellos, son duales de las que se obtienen de aplicar la 2ª/1ª ley de Kirchhoff a todas las mallas (incluida la exterior)/nudos, del otro. Como consecuencia de la definición dada, dos configuraciones duales tendrán el mismo número de ramas y el número de nudos/mallas de una será igual al de mallas/nudos de la otra (teniendo en cuenta la malla externa).
Elementos duales:
Son aquellos cuyas ecuaciones de definición son duales. Así, un condensador y una bobina son duales. Una resistencia y una conductancia son duales. Una fuente de tensión es dual de una fuente de intensidad y un cortocircuito es dual de un circuito abierto.
Circuitos duales:
Dos circuitos son duales cuando sus configuraciones o grafos lo son y, además, las ramas duales están formadas por elementos duales (el ejemplo más conocido es el de los circuitos Thevenin/Norton).
Ejemplo: Circuitos serie y paralelo R-C-L.
El circuito dual del representado en la Fig. 11 es el de la Fig. 12.
En él se cumple:
Mientras que el circuito de la Fig. 12 cumple:
Como se ve, la ecuacion 10 es dual de la 9 y, por tanto, también lo serán las configuraciones de las Fig. 11 y 12, cuyo comportamiento definen.
Podemos afirmar, en general, que las configuraciones serie y paralelo son duales. Como las ramas del circuito serie están formadas por los elementos duales de las del circuito paralelo, ambos son duales. Si, para dos circuitos duales, el primero se analiza por el método de mallas y el segundo por el de nudos, tomando como nudo de referencia, para el segundo, el dual de la malla exterior del primero, las ecuaciones que resultan para ambos, tienen la misma forma.
1ª Ley: La suma algebraica de las intensidades que circulan por todas las ramas que cortan un recinto cerrado es igual a cero: Σi = 0.
2ª Ley: La suma algebraica de las tensiones de las ramas que forman un circuito cerrado es igual a cero: Σu = 0.
Se observa la dualidad entre estas leyes básicas con las palabras tensiónintensidad y recinto cerrado-circuito cerrado que pueden considerarse como conceptos duales básicos.
Como se ve, la dualidad queda reflejada en las ecuaciones matemáticas, por simple intercambio de las variables duales.
Configuraciones duales:
Considerando el espacio exterior de todo circuito plano como una malla adicional (supóngase que el circuito reposa sobre una esfera)limitada por las ramas externas, se dice que dos circuitos tienen configuraciones duales cuando las ecuaciones que resultan de aplicar la 1ª/2ª ley de Kirchhoff a todos los nudos/mallas (incluida la exterior), de uno de ellos, son duales de las que se obtienen de aplicar la 2ª/1ª ley de Kirchhoff a todas las mallas (incluida la exterior)/nudos, del otro. Como consecuencia de la definición dada, dos configuraciones duales tendrán el mismo número de ramas y el número de nudos/mallas de una será igual al de mallas/nudos de la otra (teniendo en cuenta la malla externa).
Elementos duales:
Son aquellos cuyas ecuaciones de definición son duales. Así, un condensador y una bobina son duales. Una resistencia y una conductancia son duales. Una fuente de tensión es dual de una fuente de intensidad y un cortocircuito es dual de un circuito abierto.
Circuitos duales:
Dos circuitos son duales cuando sus configuraciones o grafos lo son y, además, las ramas duales están formadas por elementos duales (el ejemplo más conocido es el de los circuitos Thevenin/Norton).
Ejemplo: Circuitos serie y paralelo R-C-L.
El circuito dual del representado en la Fig. 11 es el de la Fig. 12.
En él se cumple:
Mientras que el circuito de la Fig. 12 cumple:
Como se ve, la ecuacion 10 es dual de la 9 y, por tanto, también lo serán las configuraciones de las Fig. 11 y 12, cuyo comportamiento definen.
Podemos afirmar, en general, que las configuraciones serie y paralelo son duales. Como las ramas del circuito serie están formadas por los elementos duales de las del circuito paralelo, ambos son duales. Si, para dos circuitos duales, el primero se analiza por el método de mallas y el segundo por el de nudos, tomando como nudo de referencia, para el segundo, el dual de la malla exterior del primero, las ecuaciones que resultan para ambos, tienen la misma forma.
Low Frequency Prescaler
For multiplying frequencies in the 1-to 150-Hz range, this circuit uses a 4046B and a divide 100 prescaler. The VCO output is phaselocked to the low-frequency input. This simplifies use of a frequency counter to measure LF signal frequencies. By using a 4017B and a 1-kHz fIN, the circuit can be used as a 1-to 9-kHz frequency synthesizer or as a x10 frequency multiplier.
10Mhz Frequency Counter
The circuit consists of ICM7208 seven-decade counter U1, ICM7207 oscillator controller U2, and CA3130 BIFET op amp U3. IC U1 counts input signals, decodes them to 7-segment format, and outputs signals that are used to drive a 7-digit display. IC U2 provides the timing for U1, while U3 conditions the input to U1. The 5.24288-MHz crystal frequency is divided by U2 to produce a 1280-MHz multiplexing signal at pin 12 of U2. That signal is input to pin 16 and used to scan the display digits in sequence.
1.2Ghz Frequency Counter
The output of the CA 3179 is fed through the D1/Q1 circuit. Those components serve to boost the 1-V output of the CA3179 to a standard TTL level. Then, depending on the position of range switch S2b, the signal is passed directly to the 7216, or through the divide-by-four circuit built from the two D flip-flops in IC3.
The other half of the range switch S2a controls the voltage at pin 3 of the CA3179. When pin 3 is high, the signal applied to pin 9 is fed through an extra internal divide-by-four stage before it is amplified and output on pins 4 and 5 . When pin 3 is low, the signal on pin 13 is simply processed for output without being divided internally.
A 3.90625-MHZ crystal provides the time base: the crystal yields gate time of 0.256 second. The displayed frequency equals the input frequency divided by 1000 in the fast mode. In slow mode, gate time is 2.56 seconds. The displayed frequency equals the input frequency divided by 100 in the slow mode.
Switch S4, gate time, performs two functions. First it selects the appropriate gate time according to which digit output of IC1 the range input is connected to. Another of the 7216's inputs is also controlled by S4: the DP select input. The decimal point of the digit output to which that pin is connected will be the one that lights up. The correct decimal point illuminates, according to the position of S4, to provide a reading in MHz.
The other half of the range switch S2a controls the voltage at pin 3 of the CA3179. When pin 3 is high, the signal applied to pin 9 is fed through an extra internal divide-by-four stage before it is amplified and output on pins 4 and 5 . When pin 3 is low, the signal on pin 13 is simply processed for output without being divided internally.
A 3.90625-MHZ crystal provides the time base: the crystal yields gate time of 0.256 second. The displayed frequency equals the input frequency divided by 1000 in the fast mode. In slow mode, gate time is 2.56 seconds. The displayed frequency equals the input frequency divided by 100 in the slow mode.
Switch S4, gate time, performs two functions. First it selects the appropriate gate time according to which digit output of IC1 the range input is connected to. Another of the 7216's inputs is also controlled by S4: the DP select input. The decimal point of the digit output to which that pin is connected will be the one that lights up. The correct decimal point illuminates, according to the position of S4, to provide a reading in MHz.
Voltage to Pulse Duration Converter
Voltage levels can be converted to pulse durations by combining an op amp and a timer IC. Accuracies to better than 1% can be obtained with this circuit (a), and the output signals (b) still retain the original frequency, independent of the input voltage.
Voltage to Current Converter 2
The current out is Iout =Vin/R. For negative currents, a PNP can be used and, for better accuracy, a Darlington pair can be substituted for the transistor. With careful design, this circuit can be used to control currents of many amps. Unity gain compensation is necessary.
Voltage to Current Converter
This voltage to current converter uses three op amps to drive a pair of power transistors. The current output is calculated as:
Iout = Vin / R6
Output resistance is over 50 Mohms. Iout can range from 1 mA to the current ratings of T1 and T2.
Iout = Vin / R6
Output resistance is over 50 Mohms. Iout can range from 1 mA to the current ratings of T1 and T2.
VLF Converter
The VLF Converter can be used to pick up signals for the general coverage of shortwave receivers. A number of unusual signals can be heard on frequencies below 15 kHz. This converter will convert frequencies from 0 to 250 kHz to 3500 to 3750 kHz so that the LF- and VLF-band segments can be received on an amateur or shortwave receiver that covers 3500 to 400 kHz. Signals from a short whip antenna (8 to 10 feet) are coupled through low-pass filter L1/L2/C2/C3 to RF amp Q1. Q3 mixes these signals with a 3.5-MHz signal from Q2 and associated components C4, R5, R4 and 3.5-MHz XTAL. L3 is an RF choke that presents an inductive load to Q3. It should be resonant somewhat above 3.5 MHz when placed in the circuit. An adjustable coil of about 30 to 100uH should be sufficient. The converter output is taken from the emitter of Q3 through C6.
Temperature to Frequency Converter
In this circuit an LM34 or LM35 produces a frequency proportional to temperature. Reference current (138mA) is set via R3. The output can be used to drive a display, frequency counter, or other indicating device for temperature readout.
Sine Wave / Square Wave Converter
An op amp used as a comparator produces a 10-V p-p square-wave output with 100-mV input, to 15 kHz. Adjust R5 for symmetry of square wave at low input levels.
Shortwave Converter for AM Car Radios
Using a Signetics NE602, this converter tunes the 9.5- to 9.8 MHz range. An AM car radio is used as a tunable IF amplifier. Output is taken from J2, the auto antenna. The crystal (XTAL1) can be a frequency about 1 MHz below the desired tuning range; for 9.5 to 9.8 MHz, an 8.5- to 8.8-MHz crystal should be used.
Power Voltage to Current Converter
Low cost converter is capable of supplying constant ac currents up to 1 A over variable loads.
Positive to Negative Converter
The transformerless dc-dc converter derives a negative supply voltage from a positive. As a bonus, the circuit also generates a clock signal. The negative output voltage tracks the dc-input voltage linearity (a), but its magnitude is about 3 V lower. Application of a 500-W load, (b), causes 10% change from the no-load value.
Period to Voltage Converter
ICA, R1, R2, R3, and Q1 form a current source. The current that charges C1 is given by:
I= VDN x R1
(R1+R2) x R3
= 15 x 3 kW
(3kW +12kW) x 470kW
= 6.4mA
The input signal drives ICD. Because ICD's positive input (V+) is slightly offset to +0.1V, its steady state output will be around +13V. This voltage is send to ICC thorough D2, setting ICC's output to +13V. Therefore, point D is cut off by D1, and C1 is charged by the current source. Assuming the initial voltage on C1 is zero, the maximum voltage (VCmax) is given by:
VCMAX= I x T
C1
= 6.4 x t
0.0047
= 1326t
If t=1 ms, then VCmax=1.362V
When the input goes from low to high, a narrow positive pule is generated at point A. This pulse becomes - 13V at point B, which cuts off D2. ICC's V+ voltage becomes zero. The charge on C1 will be absorbed by ICC on in a short time. The time constant of C2 and R5 determines the discharge period -- about 10us. ICB is a buffer whose gain is equal to (R8+R9)/R9=1.545. ICD's average voltage will be (1362t x 1.545)/2=1052t. R10 and C3 smooth the sawtooth waveform to a dc output.
I= VDN x R1
(R1+R2) x R3
= 15 x 3 kW
(3kW +12kW) x 470kW
= 6.4mA
The input signal drives ICD. Because ICD's positive input (V+) is slightly offset to +0.1V, its steady state output will be around +13V. This voltage is send to ICC thorough D2, setting ICC's output to +13V. Therefore, point D is cut off by D1, and C1 is charged by the current source. Assuming the initial voltage on C1 is zero, the maximum voltage (VCmax) is given by:
VCMAX= I x T
C1
= 6.4 x t
0.0047
= 1326t
If t=1 ms, then VCmax=1.362V
When the input goes from low to high, a narrow positive pule is generated at point A. This pulse becomes - 13V at point B, which cuts off D2. ICC's V+ voltage becomes zero. The charge on C1 will be absorbed by ICC on in a short time. The time constant of C2 and R5 determines the discharge period -- about 10us. ICB is a buffer whose gain is equal to (R8+R9)/R9=1.545. ICD's average voltage will be (1362t x 1.545)/2=1052t. R10 and C3 smooth the sawtooth waveform to a dc output.
One Chip Crystal Controlled Converter
This circuit can work over a wide range of frequencies. XTAL 1 is a fundamental-frequency crystal. T1 and C1 are tuned to the input frequency. An application of this circuit is a simple shortwave converter for AM radios, etc. A tunable oscillator can also be used, as shown.
Low Noise 420Mhz ATV Receiver/Converter
L1, Q1, L2 and L3 compose an RF amplifier stage that feeds M1, a doubly balanced mixer. Q4 is a local oscillator stage in the 375-MHz range. Signals in the 420- to 450-MHz range from Q1 are mixed in M1 and fed through filter L6/L7/C17, where only the 60- to 70-MHz (CH3/CH4) signals pass. The IF signal is passed to Q3, and IF amplifier. The overall gain is 25 dB and the noise figure less then 2 dB.
Low Frequency Converter
Among the signals below 550kHz are maritime mobile, distress, radio beacons, aircraft weather, European Longwave-AM broadcast, and point-to-point communications. The low-frequency converter converts the 10 to 500kHz LW range to a 1010 to 1550 kHz MW range, by adding 1000kHz to all received signals.
Radio calibration is unnecessary because signals are received at the AM-radio's dial setting, plus 1MHz; a 100-kHz signal is received at 1100kHz, a 335-kHz signal at 1335kHz, etc. The low-frequency signals are fed to IC1, a doubly-balanced mixer.
Transistor Q2 and associated circuitry form a Hartley 1000-kHz local oscillator, which is coupled from Q2's drain, through C8, to IC1 pin 8. Signals in the 10-550 kHz range are converted to 1010-1550 kHz. The mixer heterodynes the incoming low-frequency signal and local-oscillator signal. Transistor Q3 reduces IC1's high-output impedance to about 100 ohms to match most receiver inputs. Capacitor C15 couples the 1010-1550 kHz frequencies from Q's emitter to output jack J3, while blocking any dc basis.
Inductor L6 couples the dc voltage that's carried in the RF signal cable from the rcvr/dc adaptor, The dc voltage and RF signals don't interfere with one another; that saves running a separate power-supply wire, which simplifies installation at a remote location. Capacitors C14 and C13 provide dc supply filtering.
Radio calibration is unnecessary because signals are received at the AM-radio's dial setting, plus 1MHz; a 100-kHz signal is received at 1100kHz, a 335-kHz signal at 1335kHz, etc. The low-frequency signals are fed to IC1, a doubly-balanced mixer.
Transistor Q2 and associated circuitry form a Hartley 1000-kHz local oscillator, which is coupled from Q2's drain, through C8, to IC1 pin 8. Signals in the 10-550 kHz range are converted to 1010-1550 kHz. The mixer heterodynes the incoming low-frequency signal and local-oscillator signal. Transistor Q3 reduces IC1's high-output impedance to about 100 ohms to match most receiver inputs. Capacitor C15 couples the 1010-1550 kHz frequencies from Q's emitter to output jack J3, while blocking any dc basis.
Inductor L6 couples the dc voltage that's carried in the RF signal cable from the rcvr/dc adaptor, The dc voltage and RF signals don't interfere with one another; that saves running a separate power-supply wire, which simplifies installation at a remote location. Capacitors C14 and C13 provide dc supply filtering.
DC/DC Converter Circuit With 3.3 and 5V Outputs
Input voltages can range from 8 V to 30 V. The load range on the 5V is 0.05A to 5A while the 3.3-V load range is 0.1A to 1A. The circuit is self-protected under no-load conditions. Over all load and line conditions, including cross regulation, the 3.3-V output varies from 3.25V to 3.27V. The 5-V output varies from 4.81V to 5.19V under the same conditions.
In a typical application to 0.5A on the 3.3V and 0.25A on the 5V, efficiency is typically 76%. With an input voltage of 30V and a full-load condition, the efficiency drops to 66%. In normal operating regions, efficiency is always better then 70%. The 5-V ripple is less then 75mV and the 3.3-V ripple less then 50mV over all line and load conditions.
In a typical application to 0.5A on the 3.3V and 0.25A on the 5V, efficiency is typically 76%. With an input voltage of 30V and a full-load condition, the efficiency drops to 66%. In normal operating regions, efficiency is always better then 70%. The 5-V ripple is less then 75mV and the 3.3-V ripple less then 50mV over all line and load conditions.